
In WordPress, a permalink is a permanent URL that points to a specific post or page on a website. It is the web address that users can use to access the content of your website, and it remains unchanged even if the content is updated or moved.
Structure and Types
Permalinks in WordPress have a specific structure that determines how they are displayed in the browser’s address bar. The default permalink structure in WordPress includes the domain name followed by the post ID, like this: http://example.com/?p=123. However, this structure is not very user-friendly or search engine optimized.
WordPress offers several other permalink structures that are more readable and SEO-friendly, including:
- Day and name:
http://example.com/2021/08/17/sample-post/ - Month and name:
http://example.com/2021/08/sample-post/ - Numeric:
http://example.com/archives/123 - Post name:
http://example.com/sample-post/
Users can also create their own custom permalink structures using tagsIn WordPress, tags are a taxonomy used to classify and organize posts. They are similar to categories, but unl... More such as %postname%, %categoryIn WordPress, categories are a fundamental taxonomy used to group and organize posts based on their topics or ... More%, and %tag%. This allows for even greater flexibility in creating user-friendly URLs.
You can edit the permalink structure for your site by going to Settings > Permalinks from the WordPress dashboardIn WordPress, the Dashboard is a central hub for managing a website's content and settings. It is the first sc... More:
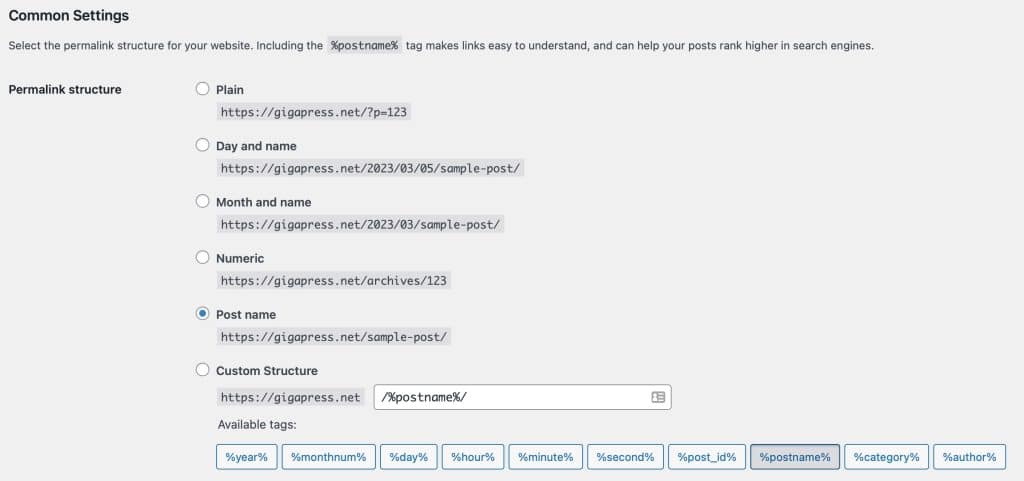
Benefits
Permalinks play an important role in SEO by providing search engines with information about the content of your website. A well-structured permalink can help improve your site’s visibility in search engine results pagesIn WordPress, a page is a content type that is used to create non-dynamic pages on a website. Pages are typica... More (SERPs) by including relevant keywords and making it easier for users to understand what your content is about.
Permalinks also make it easier for users to share links to your content on social media platforms or other websites. When someone shares a link with others, they will be able to easily return to the original content without having to search for it again.
Best Practices
When setting up permalinks on your WordPress site, there are some best practices you should follow:
- Choose a structure that is user-friendly and reflects the content of your site.
- Avoid changing permalinks once they have been published, as this can cause broken links and negatively impact SEO.
- Use descriptive titles for postsA post is a type of content in WordPress, a popular open-source content management system used for creating an... More and pages, as these will be included in the permalink structure.
- Use canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues when multiple URLs lead to the same page.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your permalinks provide both users and search engines with valuable information about your website’s content while maintaining optimal performance.
Conclusion
Permalinks are an essential part of any WordPress website, providing a permanent URL to access specific content. By choosing a user-friendly and SEO-optimized permalink structure, you can improve your site’s visibility in search engine results pages and make it easier for users to share links to your content.
Remember to follow best practices when setting up permalinks, including using descriptive titles for posts and pages, avoiding changing permalinks once they have been published, and using canonical tags to avoid duplicate content issues.
